|
Background: |
Following independence from Spain in 1816, Argentina experienced periods of internal political conflict between conservatives and liberals and between civilian and military factions. After World War II, a long period of Peronist authoritarian rule and interference in subsequent governments was followed by a military junta that took power in 1976. Democracy returned in 1983, and numerous elections since then have underscored Argentina’s progress in democratic consolidation. |
| Argentina | Geography |
|
Location: |
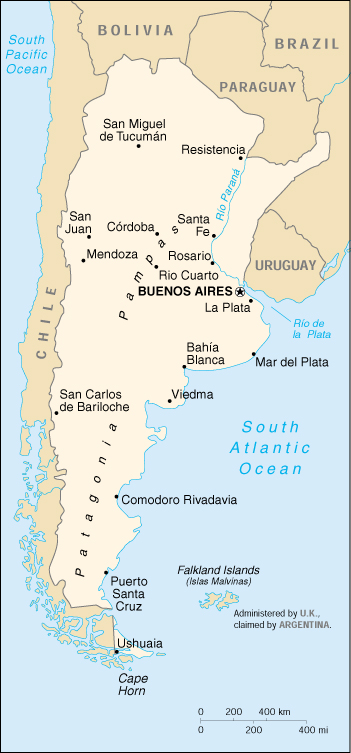
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Chile and Uruguay |
|
Geographic coordinates: |
34 00 S, 64 00 W |
|
Map references: |
South America |
|
Area: |
total: 2,780,400 sq km |
land: 2,736,690 sq km
water: 43,710 sq km
|
Area – comparative: |
slightly less than three-tenths the size of the US |
|
Land boundaries: |
total: 11,968 km |
border countries: Bolivia 942 km, Brazil 1,263 km, Chile 6,691 km, Paraguay 2,531 km, Uruguay 541 km
|
Coastline: |
4,989 km |
|
Maritime claims: |
|
||
continental shelf: 200 NM or to the edge of the continental margin
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM
|
Climate: |
mostly temperate; arid in southeast; subantarctic in southwest |
|
Terrain: |
rich plains of the Pampas in northern half, flat to rolling plateau of Patagonia in south, rugged Andes along western border |
|
Elevation extremes: |
lowest point: Salinas Chicas -40 m (located on Peninsula Valdes) |
highest point: Cerro Aconcagua 6,960 m (located in the northwestern corner of the province of Mendoza; highest point in South America)
|
Natural resources: |
fertile plains of the Pampas, lead, zinc, tin, copper, iron ore, manganese, petroleum, uranium |
|
Land use: |
arable land: 13.68%
permanent crops: 0.36%
other: 85.96% (2011)
|
|
Irrigated land: |
15,500 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards: |
San Miguel de Tucuman and Mendoza areas in the Andes subject to earthquakes; pamperos are violent windstorms that can strike the Pampas and northeast; heavy flooding |
|
Environment – current issues: |
environmental problems (urban and rural) typical of an industrializing economy such as soil degradation, desertification, air pollution, and water pollution |
note: Argentina is a world leader in setting voluntary greenhouse gas targets
|
Environment – international agreements: |
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling |
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Marine Life Conservation
|
Geography – note: |
second-largest country in South America (after Brazil); strategic location relative to sea lanes between the South Atlantic and the South Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage); Cerro Aconcagua is South America’s tallest mountain, while the Valdes Peninsula is the lowest point on the continent |
Buenos Aires City
| Argentina | People |
|
Population: |
43,024,374 (July 2014 est.) |
|
Age structure: |
0-14 years: 24.9% (male 5,486,989/female 5,233,968)
15-24 years: 15.7% (male 3,445,086/female 3,301,168)
25-54 years: 38.9% (male 8,345,893/female 8,391,445)
55-64 years: 9.1% (male 1,895,965/female 2,017,330)
65 years and over: 11.4% (male 2,036,545/female 2,869,985) (2014 est.)
|
|
Population growth rate: |
0.95% (2014 est.) |
|
Birth rate: |
16.88 births/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Death rate: |
7.34deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Net migration rate: |
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Sex ratio: |
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.7 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
|
|
Infant mortality rate: |
total: 9.96 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 11.15 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 8.71 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.)
|
|
Life expectancy at birth: |
total population: 77.51 years male: 74.28 years female: 80.91 years (2014 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate: |
2.25 children born/woman (2014 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate: |
0.4% (2012 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS: |
97,900 (2012 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – deaths: |
3,700 (2012 est.) |
|
Nationality: |
noun: Argentine(s) |
adjective: Argentine
|
Ethnic groups: |
white (mostly Spanish and Italian) 97%, mestizo (mixed white and Amerindian ancestry), Amerindian, or other non-white groups 3% |
|
Religions: |
nominally Roman Catholic 92% (less than 20% practicing), Protestant 2%, Jewish 2%, other 4% |
|
Languages: |
Spanish (official), Italian, English, German, French, indigenous (Mapudungun, Quechua) |
|
Literacy: |
definition: age 10 and over can read and write
total population: 97.9%
male: 97.8%
female: 97.9% (2011 est.)
|
Mar del plata
| Argentina | Government |
|
Country name: |
conventional long form: Argentine Republic |
conventional short form: Argentina
local long form: Republica Argentina
local short form: Argentina
|
Government type: |
republic |
|
Capital: |
name: Buenos Aires
geographic coordinates: 34 35 S, 58 40 W
time difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: none scheduled for 2014
|
|
Administrative divisions: |
23 provinces (provincias, singular – provincia), and 1 autonomous city* (distrito federal); Buenos Aires; Buenos Aires Capital Federal*; Catamarca; Chaco; Chubut; Cordoba; Corrientes; Entre Rios; Formosa; Jujuy; La Pampa; La Rioja; Mendoza; Misiones; Neuquen; Rio Negro; Salta; San Juan; San Luis; Santa Cruz; Santa Fe; Santiago del Estero; Tierra del Fuego, Antartica e Islas del Atlantico Sur; Tucuman |
note: the US does not recognize any claims to Antarctica
|
Independence: |
9 July 1816 (from Spain) |
|
National holiday: |
Revolution Day, 25 May (1810) |
|
Constitution: |
1 May 1853; revised August 1994 |
|
Legal system: |
civil law system based on West European legal systems; note – as of January 2013, Congress was deliberating a government-backed reform to the civil code |
|
Suffrage: |
18-70 years of age; universal and compulsory; 16-17 years of age – optional |
|
Executive branch: |
chief of state: President Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER (since 10 December 2007); Vice President Amado BOUDOU (since 10 December 2011); note – the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER (since 10 December 2007); Vice President Amado BOUDOU (since 10 December 2011)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website elections: president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for four-year terms (eligible for a second consecutive term); election last held on 23 October 2011 (next election to be held in October 2015)
election results: Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER reelected president; percent of vote – Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER 54%, Hermes BINNER 16.9%, Ricardo ALFONSIN 11.1%, Alberto Rodriguez SAA 8%, Eduardo DUHALDE 5.9%, other 4.1%
|
|
Legislative branch: |
bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of the Senate (72 seats; members are elected by direct vote; presently one-third of the members elected every two years to serve six-year terms) and the Chamber of Deputies (257 seats; members are elected by direct vote; one-half of the members elected every two years to serve four-year terms)
elections: Senate – last held on 27 October 2013 (next to be held October 2015); Chamber of Deputies – last held on 27 October 2013 (next to be held October 2015)
election results: Senate – percent of vote by bloc or party – NA; seats by bloc or party – FpV 32, UCR 17, dissident Peronists 7, FAP and UNEN 7, FpV allies 6, PRO and allies 3, other 6; Chamber of Deputies – percent of vote by bloc or party – NA; seats by bloc or party – FpV 18, FpV allies 14, UCR 10, dissident Peronists 34, FAP and UNEN 21, PRO 16, CC 3, other 14
|
|
Judicial branch: |
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (consists of the court president, vice-president, and 5 judges)
note – Argentina has a system of federal and provincial courts
judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the president and approved by the Senate; judges serve for life
subordinate courts: federal level appellate, district, and territorial courts; provincial level supreme, appellate, and first instance courts
|
|
Political parties and leaders: |
Broad Progressive Front or FAP [Hermes BINNER]
Civic Coalition or CC (a broad coalition loosely affiliated with Elisa CARRIO)
Dissident Peronists (PJ Disidente) or Federal Peronism (a sector of the Justicialist Party opposed to the Kirchners)
Front for Victory or FpV (a broad coalition, including elements of the PJ, UCR, and numerous provincial parties) [Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER]
Peronist (or Justicialist) Party or PJ [vacant]
Radical Civic Union or UCR [Mario BARLETTA]
Republican Proposal or PRO [Mauricio MACRI]
Socialist Party or PS [Ruben GIUSTINIANI]
numerous provincial parties
|
|
Political pressure groups and leaders: |
Argentine Association of Pharmaceutical Labs (CILFA)
Argentine Industrial Union (manufacturers’ association)
Argentine Rural Confederation or CRA (small to medium landowners’ association)
Argentine Rural Society (large landowners’ association)
Central of Argentine Workers or CTA (a union for employed and unemployed workers)
General Confederation of Labor or CGT (Peronist-leaning umbrella labor organization)
Roman Catholic Church
White and Blue CGT (dissident CGT labor confederation)
other: business organizations, Peronist-dominated labor movement, Piquetero groups (popular protest organizations that can be either pro or anti-government), students
|
|
International organization participation: |
AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BCIE, BIS, CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, FATF, G-15, G-20, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina (observer), UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US: |
|
||
|
Diplomatic representation from the US: |
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’Affaires Kevin K. SULLIVAN (since June 2013)
embassy: Avenida Colombia 4300, C1425GMN Buenos Aires
mailing address: international mail: use embassy street address; APO address: US Embassy Buenos Aires, Unit 4334, APO AA 34034
telephone: [54] (11) 5777-4533
FAX: [54] (11) 5777-4240
|
|
Flag description: |
three equal horizontal bands of light blue (top), white, and light blue; centered in the white band is a radiant yellow sun with a human face known as the Sun of May; the colors represent the clear skies and snow of the Andes; the sun symbol commemorates the appearance of the sun through cloudy skies on 25 May 1810 during the first mass demonstration in favor of independence; the sun features are those of Inti, the Inca god of the sun |
Cataratas del Iguazu
| Argentina | Economy |
|
Economy – overview: |
Argentina benefits from rich natural resources, a highly literate population, an export-oriented agricultural sector, and a diversified industrial base. Although one of the world’s wealthiest countries 100 years ago, Argentina suffered during most of the 20th century from recurring economic crises, persistent fiscal and current account deficits, high inflation, mounting external debt, and capital flight. A severe depression, growing public and external indebtedness, and an unprecedented bank run culminated in 2001 in the most serious economic, social, and political crisis in the country’s turbulent history. Interim President Adolfo RODRIGUEZ SAA declared a default – at the time the largest ever – on the government’s foreign debt in December of that year, and abruptly resigned only a few days after taking office. His successor, Eduardo DUHALDE, announced an end to the peso’s decade-long 1-to-1 peg to the US dollar in early 2002. The economy bottomed out that year, with real GDP 18% smaller than in 1998 and almost 60% of Argentines under the poverty line. Real GDP rebounded to grow by an average 8.5% annually over the subsequent six years, taking advantage of previously idled industrial capacity and labor, an audacious debt restructuring and reduced debt burden, excellent international financial conditions, and expansionary monetary and fiscal policies. Inflation also increased, however, during the administration of President Nestor KIRCHNER, which responded with price restraints on businesses, as well as export taxes and restraints, and beginning in 2007, with understating inflation data. Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER succeeded her husband as President in late 2007, and the rapid economic growth of previous years began to slow sharply the following year as government policies held back exports and the world economy fell into recession. The economy in 2010 rebounded strongly from the 2009 recession, but has slowed since late 2011 even as the government continued to rely on expansionary fiscal and monetary policies, which have kept inflation in the double digits. The government expanded state intervention in the economy throughout 2012. In May 2012 the Congress approved the nationalization of the oil company YPF from Spain’s Repsol. The government expanded formal and informal measures to restrict imports during the year, including a requirement for pre-registration and pre-approval of all imports. In July 2012 the government also further tightened currency controls in an effort to bolster foreign reserves and stem capital flight. During 2013, the government continued with a mix expansionary fiscal and monetary policies and foreign exchange and imports controls to limit the drain in Central Bank foreign reserves, which nevertheless dropped US $12 billion during the year. GDP grew 3% and inflation remained steady at 25%, according to private estimates. In October 2013, the government settled long-standing international arbitral disputes (including with three US firms) dating back to before and following the 2002 Argentine financial crisis. In early 2014, the government embraced a series of more orthodox economic policies. It devalued the peso 20%, substantially tightened monetary and fiscal policies, and took measures to mend ties with the international financial community, including: engaging with the IMF to improve its economic data reporting, reaching a compensation agreement with Repsol for the expropriation of YPF, and presenting a proposal to pay its arrears to the Paris Club. |
|
GDP: |
$484.6 billion (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – real growth rate: |
3.5% (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – per capita: |
$18,600 (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – composition by sector of origen: |
agriculture: 9.3%
industry: 29.7%
services: 61% (2013 est.)
|
|
Population below poverty line: |
30%
note: data are based on private estimates (2010)
|
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share: |
lowest 10%: 1.5%
highest 10%: 32.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices): |
20.8% (2013 est.) |
|
Labor force: |
17.32 millionnote: urban areas only (2013 est.) |
|
Labor force – by occupation: |
agriculture: 5%
industry: 23%
services: 72% (2009 est.)
|
|
Unemployment rate: |
7.5% (2013 est.) |
|
Budget: |
|
||
|
Industries: |
food processing, motor vehicles, consumer durables, textiles, chemicals and petrochemicals, printing, metallurgy, steel |
|
Industrial production growth rate: |
2.7%note: based on private sector estimates (2013 est.) |
|
Electricity – production: |
119.3 billion kWh (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – production by source: |
fossil fuel: 66.2% of total installed capacity (2010 est.) hydro: 27.6% of total installed capacity (2010 est.) nuclear: 3.1% of total installed capacity (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – consumption: |
111.1 billion kWh (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – exports: |
1.701 billion kWh (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – imports: |
10.3 billion kWh (2010 est.) |
|
Agriculture – products: |
sunflower seeds, lemons, soybeans, grapes, corn, tobacco, peanuts, tea, wheat; livestock |
|
Exports: |
$85.08 billion (2013 est.) |
|
Exports – commodities: |
soybeans and derivatives, petroleum and gas, vehicles, corn, wheat |
|
Exports – partners: |
Brazil 20.4%, China 7.4%, Chile 6%, US 5.2% (2012) |
|
Imports: |
$25.2 billion (f.o.b., 2000 est.) |
|
Imports – commodities: |
machinery, motor vehicles, petroleum and natural gas, organic chemicals, plastics |
|
Imports – partners: |
Brazil 27.2%, US 15.6%, China 11.9%, Germany 4.5% (2012) |
|
Debt – external: |
$111.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment- at home: |
$34.21 billion (31 December 2013 est.) |
|
Currency: |
Argentine peso (ARS) |
|
Currency code: |
ARS |
|
Exchange rates: |
Argentine pesos (ARS) per US dollar –
5.447 (2013 est.)
4.5369 (2012 est.)
3.8963 (2010 est.)
3.7101 (2009)
3.1636 (2008)
|
|
Fiscal year: |
calendar year |
Glaciar Upsula
| Argentina | Communications |
|
Telephones – main lines in use: |
10 million (2012) |
|
Telephones – mobile cellular: |
58.6 million (2012) |
|
Telephone system: |
|
||
|
broadcast media: |
government owns a TV station and a radio network; more than 2 dozen TV stations and hundreds of privately owned radio stations; high rate of cable TV subscription usage (2007) |
|
internet country code: |
ar |
|
Internet users: |
13.694 million (2009) |
|
Internet hosts: |
11.232 million (2012) |
Ciudad de la Plata
| Argentina | Transportation |
|
Railways: |
total: 36,966 km country comparison to the world: 8 broad gauge: 26,475 km 1.676-m gauge (94 km electrified)
standard gauge: 2,780 km 1.435-m gauge (42 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 7,711 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
Roadways: |
total: 231,374 km country comparison to the world: 21 paved: 69,412 km (includes 734 km of expressways)
unpaved: 161,962 km (2004)
|
|
Waterways: |
11,000 km (2012) |
|
Pipelines: |
gas 29,930 km; liquid petroleum gas 41 km; oil 6,248 km; refined products 3,631 km (2013) |
|
Ports and terminals: |
|
||
|
Merchant marine: |
total: 36 by type: bulk carrier 1, cargo 5, chemical tanker 6, container 1, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 18, refrigerated cargo 4
foreign-owned: 14 (Brazil 1, Chile 6, Spain 3, Taiwan 2, UK 2)
registered in other countries: 15 (Liberia 1, Panama 5, Paraguay 5, Uruguay 1, unknown 3) (2010)otal: 41 ships (1000 GRT or over) 435,969 GRT/707,767 DWT
by type: bulk carrier 2, cargo 10, chemical tanker 1, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 3, petroleum tanker 21, refrigerated cargo 2, roll on/roll off 1 |
|
Airports: |
1,138 (2013) |
|
Airports – with paved runways: |
|
||
|
Airports – with unpaved runways: |
total: 977
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 43
914 to 1,523 m: 484
under 914 m:
448 (2013)
|
Antartida
| Argentina | Military |
|
Military branches: |
Argentine Army (Ejercito Argentino), Navy of the Argentine Republic (Armada Republica; includes naval aviation and naval infantry), Argentine Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Argentina, FAA) (2013) |
|
Military service age and obligation: |
18-24 years of age for voluntary military service (18-21 requires parental consent); no conscription; if the number of volunteers fails to meet the quota of recruits for a particular year, Congress can authorize the conscription of citizens turning 18 that year for a period not exceeding one year (2012) |
|
Military manpower – availability: |
males age 16-49: 10,038,967
females age 16-49: 9,959,134 (2010 est.)
|
|
Military manpower – fit for military service: |
males age 16-49: 8,458,362
females age 16-49: 8,414,460 (2010 est.)
|
|
Military manpower – reaching military age annually: |
|
||
|
Military expenditures : |
0.91% of GDP (2012) |
San Luis
| Argentina | Transnational Issues |
|
Disputes – international: |
Argentina continues to assert its claims to the UK-administered Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas), South Georgia, and the South Sandwich Islands in its constitution, forcibly occupying the Falklands in 1982, but in 1995 agreed to no longer seek settlement by force; UK continues to reject Argentine requests for sovereignty talks; territorial claim in Antarctica partially overlaps UK and Chilean claims; uncontested dispute between Brazil and Uruguay over Braziliera/Brasiliera Island in the Quarai/Cuareim River leaves the tripoint with Argentina in question; in 2010, the ICJ ruled in favor of Uruguay’s operation of two paper mills on the Uruguay River, which forms the border with Argentina; the two countries formed a joint pollution monitoring regime; the joint boundary commission, established by Chile and Argentina in 2001 has yet to map and demarcate the delimited boundary in the inhospitable Andean Southern Ice Field (Campo de Hielo Sur); contraband smuggling, human trafficking, and illegal narcotic trafficking are problems in the porous areas of the border with Bolivia |
|
Illicit drugs: |
a transshipment country for cocaine headed for Europe, heroin headed for the US, and ephedrine and pseudoephedrine headed for Mexico; some money-laundering activity, especially in the Tri-Border Area; law enforcement corruption; a source for precursor chemicals; increasing domestic consumption of drugs in urban centers, especially cocaine base and synthetic drugs (2008) |
Thanks to: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html
 )
)