|
Chile |
Introduction |
|
Background: |
Prior to the coming of the Spanish in the 16th century, northern Chile was under Inca rule while Araucanian Indians inhabited central and southern Chile; the latter were not completely subjugated by Spain until the early 1880s. Although Chile declared its independence in 1810, decisive victory over the Spanish was not achieved until 1818. In the War of the Pacific (1879-84), Chile defeated Peru and Bolivia and won its present northern lands. A three-year-old Marxist government of Salvador ALLENDE was overthrown in 1973 by a dictatorial military regime led by Augusto PINOCHET, who ruled until a freely elected president was installed in 1990. Sound economic policies, maintained consistently since the 1980s, have contributed to steady growth and have helped secure the country’s commitment to democratic and representative government. Chile has increasingly assumed regional and international leadership roles befitting its status as a stable, democratic nation.
Santiago |
|
Chile |
Geography |
|
Location: |
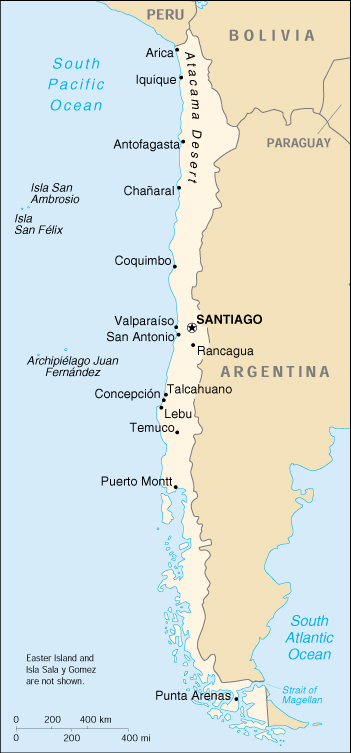
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru |
|
Geographic coordinates: |
30 00 S, 71 00 W |
|
Map references: |
South America |
|
Area: |
total: 756,102 sq km land: 743,812 sq km water: 12,290 sq km
note: includes Easter Island (Isla de Pascua) and Isla Sala y Gomez
|
|
Area – comparative: |
slightly smaller than twice the size of Montana |
|
Land boundaries: |
total: 7,801 km border countries: Argentina 6,691 km, Bolivia 942 km, Peru 168 km |
|
Coastline: |
6,435 km |
|
Maritime claims: |
contiguous zone: 24 NM continental shelf: 200/350 NM exclusive economic zone: 200 NM territorial sea: 12 NM |
|
Climate: |
temperate; desert in north; Mediterranean in central region; cool and damp in south |
|
Terrain: |
low coastal mountains; fertile central valley; rugged Andes in east |
|
Elevation extremes: |
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m highest point: Nevado Ojos del Salado 6,880 m |
|
Natural resources: |
copper, timber, iron ore, nitrates, precious metals, molybdenum, hydropower |
|
Land use: |
arable land: 1.74% permanent crops: 0.6%
other: 97.65% (2011)
|
|
Irrigated land: |
19,000 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards: |
severe earthquakes; active volcanism; tsunamis |
|
Environment – current issues: |
air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage |
|
Environment – international agreements: |
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban |
|
Geography – note: |
the longest north-south trending country in the world, extending across 38 degrees of latitude; strategic location relative to sea lanes between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage); Atacama Desert – the driest desert in the world – spreads across the northern part of the country; the crater lake of Ojos del Salado is the world’s highest lake (at 6,390 m)
Viña del Mar |
|
Chile |
People |
|
Population: |
17,363,894 (July 2014 est.) |
|
Age structure: |
0--14 years: 20.7% (male 1,834,247/female 1,760,315) 15-24 years: 16.3% (male 1,442,610/female 1,383,738)
25-54 years: 43.2% (male 3,733,261/female 3,766,912)
55-64 years: 9.9% (male 806,044/female 910,818)
65 years and over: 9.7% (male 720,681/female 1,005,268) (2014 est.)
|
|
Population growth rate: |
0.84% (2014 est.) |
|
Birth rate: |
13.97 births/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Death rate: |
5.93 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Net migration rate: |
0.35 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.) |
|
Sex ratio: |
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
|
|
Infant mortality rate: |
total: 7.02 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth: |
total population: 78.44 years |
|
Total fertility rate: |
1.84 children born/woman (2014 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate: |
0.4% (2012 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS: |
38,700 (2012 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS – deaths: |
NA |
|
Nationality: |
noun: Chilean(s) adjective: Chilean |
|
Ethnic groups: |
white and non-indigenous 88.9%, Mapuche 9.1%, Aymara 0.7%, other indigenous groups 1% (includes Rapa Nui, Likan Antai, Quechua, Colla, Diaguita, Kawesqar, Yagan or Yamana), unspecified 0.3% (2012 est.) |
|
Religions: |
Roman Catholic 66.7%, Evangelical or Protestant 16.4%, Jehovah’s Witnesses 1%, other 3.4%, none 11.5%, unspecified 1.1% (2012 est.) |
|
Languages: |
Spanish 99.5% (official), English 10.2%, indigenous 1% (includes Mapudungun, Aymara, Quechua, Rapa Nui), other 2.3%, unspecified 0.2% |
|
Literacy: |
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
|
|
Chile |
Government |
|
Country name: |
conventional long form: Republic of Chile conventional short form: Chile local long form: Republica de Chile local short form: Chile |
|
Government type: |
republic |
|
Capital: |
Santiago |
|
Administrative divisions: |
15 regions (regiones, singular – region); Aysen, Antofagasta, Araucania, Arica y Parinacota, Atacama, Biobio, Coquimbo, Libertador General Bernardo O’Higgins, Los Lagos, Los Rios, Magallanes y de la Antartica Chilena, Maule, Region Metropolitana (Santiago), Tarapaca, Valparaiso note: the US does not recognize claims to Antarctica
|
|
Independence: |
18 September 1810 (from Spain) |
|
National holiday: |
Independence Day, 18 September (1810) |
|
Constitution: |
many previous, latest adopted 11 September 1980, effective 11 March 1981, amended many times, last in 2011 (2011) |
|
Legal system: |
civil law system influenced by several West European civil legal systems; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional Tribunal |
|
Suffrage: |
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch: |
chief of state: President Michelle BACHELET Jeria (since 11 March 2014); note – the president is both the chief of state and head of government head of government: President Michelle BACHELET Jeria (since 11 March 2014)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
elections: president elected by popular vote for a single four-year term; election last held on 17 November 2013 with a runoff election held on 15 December 2013 (next to be held on 19 November 2017)
election results: Michelle BACHELET Jeria elected president; percent of vote – Michelle BACHELET Jeria 62.2%; Evelyn Rose MATTHEI Fornet 37.8%
|
|
Legislative branch: |
bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of the Senate or Senado (38 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve eight-year terms; one-half elected every four years) and the Chamber of Deputies or Camara de Diputados (120 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms) elections: Senate – last held on 13 December 2009 (next to be held in November 2013); Chamber of Deputies – last held on 13 December 2009 (next to be held in November 2013)
election results: Senate – percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – CPD 9 (PDC 4, PPD 3, PS 2), APC 9 (RN 6, UDI 3); Chamber of Deputies – percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – APC 58 (UDI 37, RN 18, other 3), CPD 57 (PDC 19, PPD 18, PS 11, PRSD 5, PC 3, other 1), PRI 3, independent 2; note – as of 19 February 2013, the composition of the entire legislature is as follows: Senate – seats by party – CPD 19 (PDC 9, PPD 4, PS 5, PRSD 1), Coalition for Change (former APC) 16 (RN 8, UDI 8), independent 2, MAS 1; Chamber of Deputies – seats by party – Coalition for Change (former APC) 56 (UDI 39, RN 17), CPD 53 (PDC 19, PPD 18, PS 11, PRSD 5), independent 5, PC 3, PRI 2, IC 1
|
|
Judicial branch: |
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (consists of a court president and 20 members or ministros); Constitutional Court (consists of 7 members); Electoral Court (consists of 5 members) judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president and ratified by the Senate from lists of candidates provided by the court itself; judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 70; Constitutional Court members appointed – 3 by the Supreme Court, 1 by the president of the republic, 2 by the National Security Council, and 1 by the Senate; members serve 8-year terms with partial court replacement every 4 years (the court reviews constitutionality of legislation); Electoral Court member appointments – 4 by the Supreme Court and 1 a former president or vice-president of the Senate or Chamber of Deputies selected by the Supreme Court; member term NA
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; oral criminal tribunals; military tribunals; local police courts; specialized tribunals and courts in matters such as family, labor, customs, taxes, and electoral affairs
|
|
Political parties and leaders: |
Broad Social Movement or MAS [Alejandro NAVARRO Brain] Citizen Left or IC
Equality Party [Lautaro GUANCA Vallejos]
Coalition for Change or CC (also known as the Alliance for Chile (Alianza) or APC) (including National Renewal or RN [Carlos LARRAIN Pena], and Independent Democratic Union or UDI [Patricio MELERO]
Coalition of Parties for Democracy (Concertacion) or CPD (including Christian Democratic Party or PDC [Ignacio WALKER Prieto], Party for Democracy or PPD [Jaime Daniel QUINTANA Leal], Radical Social Democratic Party or PRSD [Jose Antonio GOMEZ Urrutia], and Socialist Party or PS [Osvaldo ANDRADE Lara])
Communist Party of Chile (Partido Comunista de Chile) or PC [Guillermo TEILLIER del Valle]
Ecological Green Party [Cristian VILLAROEL Novoa]
Humanist Party or PH [Danilo MONTEVERDE Reyes]
Independent Regionalist Party or PRI [Carlos OLIVARES Zepeda]
Progressive Party or PRO [Marco ENRIQUEZ-OMINAMI Gumucio]
|
|
Political pressure groups and leaders: |
Roman Catholic Church, particularly conservative groups such as Opus Dei United Labor Central or CUT includes trade unionists from the country’s five largest labor confederations other: university student federations at all major universities |
|
International organization participation: |
APEC, CCC, ECLAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, RG, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMIBH, UNMOGIP, UNTAET, UNTSO, UNU, UPU, WCL, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US: |
|
||
|
Diplomatic representation from the US: |
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’Affaires Stephen M. LISTON embassy: Avenida Andres Bello 2800, Las Condes, Santiago
mailing address: APO AA 34033
telephone: [56] (2) 330-3000
FAX: [56] (2) 330-3710, 330-3160
|
|
Flag description: |
two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red; there is a blue square the same height as the white band at the hoist-side end of the white band; the square bears a white five-pointed star in the center; design was based on the US flag
|
|
Chile |
Economy |
|
Economy – overview: |
Chile has a market-oriented economy characterized by a high level of foreign trade and a reputation for strong financial institutions and sound policy that have given it the strongest sovereign bond rating in South America. Exports of goods and services account for approximately one-third of GDP, with commodities making up some three-quarters of total exports. Copper alone provides 19% of government revenue. From 2003 through 2013, real growth averaged almost 5% per year, despite the slight contraction in 2009 that resulted from the global financial crisis. Chile deepened its longstanding commitment to trade liberalization with the signing of a free trade agreement with the US, which took effect on 1 January 2004. Chile has 22 trade agreements covering 60 countries including agreements with the European Union, Mercosur, China, India, South Korea, and Mexico. Chile has joined the United States and nine other countries in negotiating the Trans-Pacific-Partnership trade agreement. The Chilean Government has generally followed a countercyclical fiscal policy, accumulating surpluses in sovereign wealth funds during periods of high copper prices and economic growth, and generally allowing deficit spending only during periods of low copper prices and growth. As of 31 December 2012, those sovereign wealth funds – kept mostly outside the country and separate from Central Bank reserves – amounted to more than $20.9 billion. Chile used these funds to finance fiscal stimulus packages during the 2009 economic downturn. In May 2010 Chile signed the OECD Convention, becoming the first South American country to join the OECD. |
|
GDP: |
$335.4 billion (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – real growth rate: |
4.4% (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – per capita: |
$19,100 (2013 est.) |
|
GDP – composition by sector: |
agriculture: 3.6% |
|
Population below poverty line: |
15.1% (2009 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share: |
lowest 10%: 1.5% |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices): |
1.7% (2013 est.) |
|
Labor force: |
8.367 million (2013 est.) |
|
Labor force – by occupation: |
agriculture: 13.2% |
|
Unemployment rate: |
6% (2013 est.) |
|
Budget: |
revenues: $58.49billion |
|
Industries: |
copper, other minerals, foodstuffs, fish processing, iron and steel, wood and wood products, transport equipment, cement, textiles |
|
Industrial production growth rate: |
3% (2013 est.) |
|
Electricity – production: |
62.86 billion kWh (2011 est.) |
|
Electricity – production by source: |
62% of total installed capacity (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – consumption: |
53.93 billion kWh (2010 est.) |
|
Electricity – exports: |
0 kWh (2012 est) |
|
Electricity – imports: |
734 million kWh (2011 est.) |
|
Agriculture – products: |
wheat, corn, grapes, beans, sugar beets, potatoes, fruit; beef, poultry, wool; fish; timber |
|
Exports: |
$77.94 billion (2013 est.) |
|
Exports – commodities: |
copper, fruit, fish products, paper and pulp, chemicals, wine |
|
Exports – partners: |
China 23.3%, US 12.3%, Japan 10.7%, South Korea 5.8%, Brazil 5.5% (2012) |
|
Imports: |
$75.7 billion (2013 est.) |
|
Imports – commodities: |
petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, electrical and telecommunications equipment, industrial machinery, vehicles, natural gas |
|
Imports – partners: |
US 22.9%, China 18.2%, Argentina 6.6%, Brazil 6.5% (2012) |
|
Debt – external: |
$119 billion (31 December 2013 est.) |
|
Currency code: |
CLP |
|
Currency: |
Chilean peso (CLP) |
|
Exchange rates: |
Chilean pesos (CLP) per US dollar – 491.7 (2013 est.)
486.49 (2012 est.)
510.25 (2010 est.)
560.86 (2009)
509.02 (2008)
|
|
Fiscal year: |
calendar year
|
|
Chile |
Communications |
|
Telephones – main lines in use: |
3.276 million (2012) |
|
Telephones – mobile cellular: |
24.13 million (2012) |
|
Telephone system: |
general assessment: privatization began in 1988; most advanced telecommunications infrastructure in South America; modern system based on extensive microwave radio relay facilities; domestic satellite system with 3 earth stations domestic: number of fixed-line connections have stagnated in recent years as mobile-cellular usage continues to increase, reaching 130 telephones per 100 persons
international: country code – 56; landing points for the Pan American, South America-1, and South American Crossing/Latin America Nautilus submarine cables providing links to the US and to Central and South America; satellite earth stations – 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)
|
|
broadcast media: |
national and local terrestrial TV channels, coupled with extensive cable TV networks; the state-owned Television Nacional de Chile (TVN) network is self financed through commercial advertising revenues and is not under direct government control; large number of privately owned TV stations; about 250 radio stations (2007) |
|
Internet country code: |
.cl |
|
Internet hosts: |
2.152 million (2012) |
|
Internet users: |
7.009 million (2009)
|
|
Chile |
Transportation |
|
Railways: |
total: 7,082 km |
|
Roadways: |
total: 77,764 km paved: 18,119 km (includes 2,387 km of expressways) unpaved: 59,645 km (2010) |
|
Ports and terminals: |
Coronel, Huasco, Lirquen, Puerto Ventanas, San Antonio, San Vicente, Valparaiso |
|
Pipelines: |
gas 3,160 km; liquid petroleum gas 781 km; oil 985 km; refined products 722 km (2013) |
|
Merchant marine: |
total: 42 by type: bulk carrier 13, cargo 5, chemical tanker 7, container 2, liquefied gas 1, passenger 3, passenger/cargo 2, petroleum tanker 8, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned: 1 (Norway 1)
registered in other countries: 52 (Argentina 6, Brazil 1, Honduras 1, Isle of Man 9, Liberia 9, Panama 14, Peru 6, Singapore 6) (2010)
|
|
Airports: |
481 (2013) |
|
Airports – with paved runways: |
total: 73 |
|
Airports – with unpaved runways: |
total: 391 2,438 to 3,047 m: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 11
914 to 1,523 m: 56
under 914 m:
319 (2013)
|
|
Chile |
Military |
|
Military branches: |
Army of the Nation, Chilean Navy (Armada de Chile, includes Naval Aviation, Marine Corps, and Maritime Territory and Merchant Marine Directorate (Directemar)), Chilean Air Force (Fuerza Aerea de Chile, FACh), Carabineros Corps (Cuerpo de Carabineros) (2011) |
|
Military service age and obligation: |
18-45 years of age for voluntary male and female military service, although the right to compulsory recruitment of males 18-45 is retained; service obligation is 12 months for Army and 22 months for Navy and Air Force (2012) |
|
Manpower – availability for military service: |
males age: 16-49: 3,621,475 females ages 16-49: 4,251,954 (2010 est.) |
|
Manpower – fit for military service: |
males age 16-49: 3,621,475 females age 16-49: 3,561,099 (2010 est.)
|
|
Manpower – reaching military age annually: |
males: 141,500 female: 135,709 (2010 est.) |
| Military expenditures – percent of GDP: | 2.04% of GDP (2012) |
|
Chile |
Transnational Issues |
|
Illicit drugs: |
|
||
|
Disputes – international: |
Chile and Peru rebuff Bolivia’s reactivated claim to restore the Atacama corridor, ceded to Chile in 1884, but Chile has offered instead unrestricted but not sovereign maritime access through Chile to Bolivian natural gas; Chile rejects Peru’s unilateral legislation to change its latitudinal maritime boundary with Chile to an equidistance line with a southwestern axis favoring Peru; in October 2007, Peru took its maritime complaint with Chile to the ICJ; territorial claim in Antarctica (Chilean Antarctic Territory) partially overlaps Argentine and British claims; the joint boundary commission, established by Chile and Argentina in 2001, has yet to map and demarcate the delimited boundary in the inhospitable Andean Southern Ice Field (Campo de Hielo Sur) |
Thanks to: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

|
INFORMACION CENSAL DE CHILE POBLACIÓN TOTAL Población Total Hombres MUJERES Total País 13.348.401 6.553.254 6.795.147 Urbana 11.140.405 5.364.760 5.775.645 Rural 2.207.996 1.188.494 1.019.502 Fuente: CENSO DE POBLACIÓN Y VIVIENDA 1992 (INE) POBLACION DE 10 AÑOS Y MAS POR CONDICION DE ALFABETISMO Población Total Hombres MUJERES ALFABETOS 10.075.471 4.908.180 5.167.261 … |
|
|
|
|
|
Casa de la Moneda, Santiago, Chile |
|
El estado de Chile es unitario y su autoridad máxima es el Presidente de la República, para el cumplimiento de los objetivos de gobierno y administración, el país se divide trece unidades territoriales menores llamadas Regiones, a cargo de un Intendente designado por el Presidente de la República. Las regiones a su vez se dividen en Provincias, a cargo de un Gobernador, y estas finalmente en Comunas dirigidas por un Alcalde, el cual es electo por votación popular.
DIVISION POLITICO ELECTORAL
El territorio de Chile se divide para elegir a sus representantes al Parlamento, en 19 Circunscripciones Senatoriales y 60 Distritos de Diputados. A cada Circunscripción Senatorial le corresponde elegir 2 senadores, y a cada Distrito 2 Diputados, en consecuencia el Senado o cámara alta, esta compuesta por 38 senadores electos y la cámara baja o de Diputados por 120 miembros. Hay que señalar sin embrago, que la constitución consagra la existencia de 9 senadores no electos por votación popular, llamados institucionales o designados.(Constitución Política)

Atacama
DIVISION DEL PODER JUDICIAL
De acuerdo a la Constitución Política del Estado y a la ley Orgánica de Tribunales, Integran el poder judicial, como tribunales ordinarios de justicia, la Corte Suprema, las Cortes de Apelaciones, los Presidentes y Ministros de Corte y los Juzgados de letras. La Corte Suprema de Justicia está conformada por 21 ministros, los cuales tienen jurisdicción a nivel nacional y corresponden a los tribunales de última instancia. Dentro de cada región existe a lo menos una Corte de Apelaciones, así todas las regiones del país tienen organismos de apelación de segunda instancia. Finalmente dentro de cada comuna existe a lo menos un juzgado de letras o juzgado de primera instancia. En resumen, existen 300 juzgados de letras con asiento en las comunas, 17 Cortes de Apelaciones y la Corte Suprema